American College of Radiology Accredited Program
Radiology or medical imaging is the area of medicine that uses X-rays, magnetic waves and ultrasound to obtain detailed images of the inside of the body. Doctors can then use those images to detect and diagnose illnesses and injuries, as well as to help develop treatment plans.
Texoma Medical Center also offers interventional radiology, where physicians use imaging equipment to aid them when performing minimally invasive procedures.
Schedule an appointment
Call 903-416-4020 to schedule an appointment for radiology services.
The Radiology Department at Texoma Medical Center is accredited in computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear medicine and ultrasound by the American College of Radiology, the largest organization of radiologists in the nation.
Evaluations by board-certified physicians and medical physicists have determined that TMC has achieved high practice standards in image quality, personnel qualifications, facility equipment, quality control procedures and quality assurance programs.
The TMC Breast Care Center has been ranked in the top 1 percent for patient experience by Press Ganey.
3 convenient locations in Texas
The Radiology Department at TMC provides imaging services to residents of Denison, TX, and the surrounding region. In addition, TMC Advanced Medical Imaging, our outpatient medical imaging facility in Sherman, TX, is recognized as one of the premier imaging centers in the area.
TMC's newest outpatient imaging facility is located at ER at Anna. Here we offer X-ray (no appointment needed), open MRI, 3D digital mammography, CT scan and ultrasound.
Types of Imaging Tests
The following tests are available at Texoma Medical Center, TMC Advanced Medical Imaging and ER at Anna.
Open MRI at ER Anna
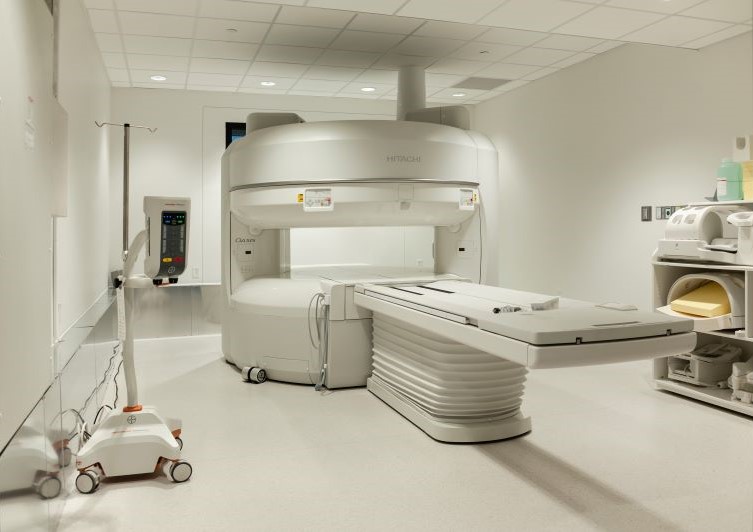
ER at Anna houses our Open MRI device located at 2710 Hackberry Drive in Anna, Texas. We know that everybody is different and not all can comfortably be examined in the same MRI system. That's why we offer an Open MRI that provides comfort, especially for anxious, claustrophobic, and bariatric patients. The open design allows patients to comfortably see all around them as high-field, advanced clinical capabilities provide the image quality physicians require.
X-ray (radiography)
X-ray (also called radiography) uses a very small dose of radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body. X-rays are the most frequently used form of medical imaging and they are also the oldest. They are often used to help see bone fracture, injuries or infections; they are also used to locate foreign objects in soft tissue.
In some cases, X-ray exams are used in conjunction with an iodine-based contrast material, which is injected, to help doctors see certain organs, blood vessels or tissue.
Computed Tomography (CT) scan
CT is an imaging test that creates detailed images of internal organs, bones and tissue. The images generated during a CT scan can be reformatted into three-dimensional images viewed on a computer monitor, printed out or transferred to other media. A CT scanner rotates around a patient's body using low radiation X-rays, to create high resolution slices (images).
Because the scanner circles a patient's body about four times every second, patients lie inside of the CT machine for two to three minutes. CT scans are performed by state-licensed, registered technologists who have specialized training and work under the supervision of board-certified radiologists.
Cardiologists may order a cardiac CT scan to get information about the presence, location and extent of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries — the vessels that supply oxygen-containing blood to the heart muscle.
The HeartFlow® Analysis
Providing a personalized 3D model of your coronary arteries, this non-invasive test shows how each blockage impacts blood flow to your heart.
Learn more about this non-invasive test →
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create clear, detailed images of internal organs and tissues. Since X-rays are not used, no radiation exposure is involved. Instead, radio waves are directed at the body. This exam takes 30-50 minutes on average and consists of several imaging series.
Many studies will require a small intravenous injection of a contrast agent. However, this agent does not contain iodine, an element used in other contrast agents for X-rays or CT scans. MRI is often used to evaluate or diagnose orthopedic (spine, extremity) or neurologic (brain, spinal cord) abnormalities.
Ultrasound (sonography)
Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to see inside the body. A transducer — a device that acts like a microphone and speaker — is placed in contact with the body using a special gel that helps transmit the sound. As the sound waves pass through the body, echoes are produced and bounce back to the transducer.
By reading the echoes, the ultrasound can produce images that illustrate the location of a structure or abnormality, as well as provide information about its composition. Ultrasound is a painless way to examine the heart, liver, pancreas, spleen, blood vessels, breast, kidney or gallbladder, and is a crucial tool for obstetrics.
Nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine, which uses radioactive material to diagnose and determine the severity of disease, offers unique diagnostic information about the function of many organs in the body that other imaging methods may not provide.
This form of imaging can often identify abnormalities very early in the progression of a disease; this enables treatment to begin at the earliest stage of a disease. Nuclear medicine is used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of diseases, including various cancers, heart disease, endocrine, gastrointestinal and neurological disorders.
Before an imaging scan, a radioactive substance called a radiopharmaceutical or radiotracer is either injected into the body, swallowed or inhaled. This material accumulates in the area of the body that will be examined. The radioactive emissions are detected by a special camera or imaging device that produces images and other information that the radiologist will analyze.
The amount of radiation from a nuclear medicine procedure is comparable to that received during a diagnostic X-ray. This amount is considered low and largely safe.
The radiopharmaceuticals emit gamma rays that can be detected by special types of cameras called: gamma camera, positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission-computed tomography (SPECT) cameras. These cameras work in conjunction with computers to form images that provide data and information about the area of body being imaged.
Note: Nuclear Medicine is not offered at ER at Anna.
Locations and hours
Texoma Medical Center
5016 South US Highway 75
Denison, TX 75020
903-416-4284
- Open 24 hours a day
- Weekend/evening appointments available for MRI, Ultrasound and CT
- Walk-ins accepted for X-rays until 5:15 p.m.
TMC Advanced Medical Imaging
2622 US Highway 75 North
Sherman, TX 75090
903-416-3730
- Open Monday – Friday, 7:30 am – 5 pm
- Walk-ins accepted for X-rays only
ER at Anna Outpatient Imaging
2710 Hackberry Drive
Anna, TX 75409
214-831-2630
- Open Monday – Friday, 8 a.m. – 5 p.m.
- Walk-ins accepted for X-rays 24/7